|





| |
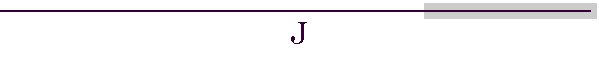
- Jactitation
- A false boast designed to increase standing at the expense of another.
This used to form the basis of an ancient legal petition called "jactitation
of marriage" wherein a person could be ordered by the courts to cease claims
of being married to a certain person when, in fact, they were not married. The
tort of
slander of title is a form of jactitation.
- J. D.
- Abbreviation for "juris doctor" or "doctor of
jurisprudence" and the formal name given to the university law degree in
the United States. It is a prerequisite to most bar admission exams.
- Joint and several liability
- Liability of more than one person for which each person may be sued for
the entire amount of damages done by all.
- Joint custody
- A child
custody decision which means that both parents share joint
legal custody
and joint
physical custody. This is not very common and many professionals have
taken to referring to "joint legal custody but sole maternal physical custody"
as "joint custody".
- Joint tenancy
- When two or more persons are equally owners of some property. The unique
aspect of joint tenancy is that as the joint tenancy owners die, their shares
accrue to the surviving owner(s) so that, eventually, the entire share is held
by one person. A valid joint tenancy is said to require the "four unities":
unity of interest (each joint tenant must have an equal interest including
equality of duration and extent), unity of title (the interests must arise
from the same document), unity of possession (each joint tenant must have an
equal right to occupy the entire property) and unity of time: the interests of
the joint tenants must arise at the same time.
- Judicial review
- When a court decision is appealed, it is known as an "appeal." But there
are many administrative agencies or
tribunals which make decisions or deliver government services of one sort
or another, the decisions of which can also be "appealed." In many cases, the
"appeal" from administrative agencies is known as "judicial review" which is
essentially a process where a court of law is asked to rule on the
appropriateness of the administrative agency or
tribunal's decision. Judicial review is a fundamental principle of
administrative law. A distinctive feature of judicial review is that the
"appeal" is not usually limited to errors in law but may be based on alleged
errors on the part of the administrative agency on findings of fact.
- Jure
- Latin, from Roman law: by right, under legal authority or by the authority
of the law. A variation, "juris" means "of right" or "of the law." See
jurisprudence below which means "science of the
law."
- Jurisdiction
- Refers to a court's authority to judge over a situation usually acquired
in one of three ways: over acts committed in a defined territory (eg. the
jurisdiction of the Supreme Court of Australia is limited to acts committed or
originating in Australia), over certain types of cases (the jurisdiction of a
bankruptcy court is limited to bankruptcy cases), or over certain persons (a
military court has jurisdiction limited to actions of enlisted personnel).
- Jurisprudence
- Technically, jurisprudence means the "science of law".
Statutes
articulate the bland rules of law, with only rare reference to factual
situations. The actual application of these statutes to facts is left to
judges who consider not only the statute but also other legal rules which
might be relevant to arrive at a judicial decision; hence, the "science".
Thus, jurisprudence" has come to refer to
case law,
or the legal decisions which have developed and which accompany statutes in
applying the law against situations of fact.
- Jury
- A group of citizens randomly selected from the general population and
brought together to assist justice by deciding which version, in their
opinion, constitutes "the truth" given different evidence by opposing parties.
- Jus
- Latin: word which, in Roman law, meant the law or a right. Also spelt "ius"
in some English translations. For example, public law was called "jus publicum"
and private law was called "jus privatum."
- Jus spatiandi et manendi
- Latin: referring to a legal right of way, and to enjoyment, granted to the
public but only for the purposes of recreation or education, such as upon
parks or public squares. Very similar to an
easement
of which some courts have said a jus spatiandi is a special type.
- Justice
- Fairness. A state of affairs in which conduct or action is both fair and
right, given the circumstances. In law, it more specifically refers to the
paramount obligation to ensure that all persons are treated fairly. Litigants
"seek justice" by asking for compensation for wrongs committed against them;
to right the inequity such that, with the compensation, a wrong has been
righted and the balance of "good" or "virtue" over "wrong" or "evil" has been
corrected.
|